What Causes IBS?
Irritible bowel syndrome is not a disease. It’s just a name given to symptoms. So if you go to doctor complaining that your bowel is irritable, they’ll give you a diagnosis of Irritable bowel Syndrome. It’s just a name for the symptoms.
Although, that’s not entirely true. There’s a test called IBSChek that can differentiate IBS. IBSChek was developed by Dr. Mark Pimmentel (a professor of Naturopathic Medicine), and looks for antibodies to Vinculin.
What is Vinculin you may ask? Vinculin is part of the Migrating Motor Complex of the small intestines. In other words, it’s part of the nerves in the intestines. So what happens is this: someone gets food 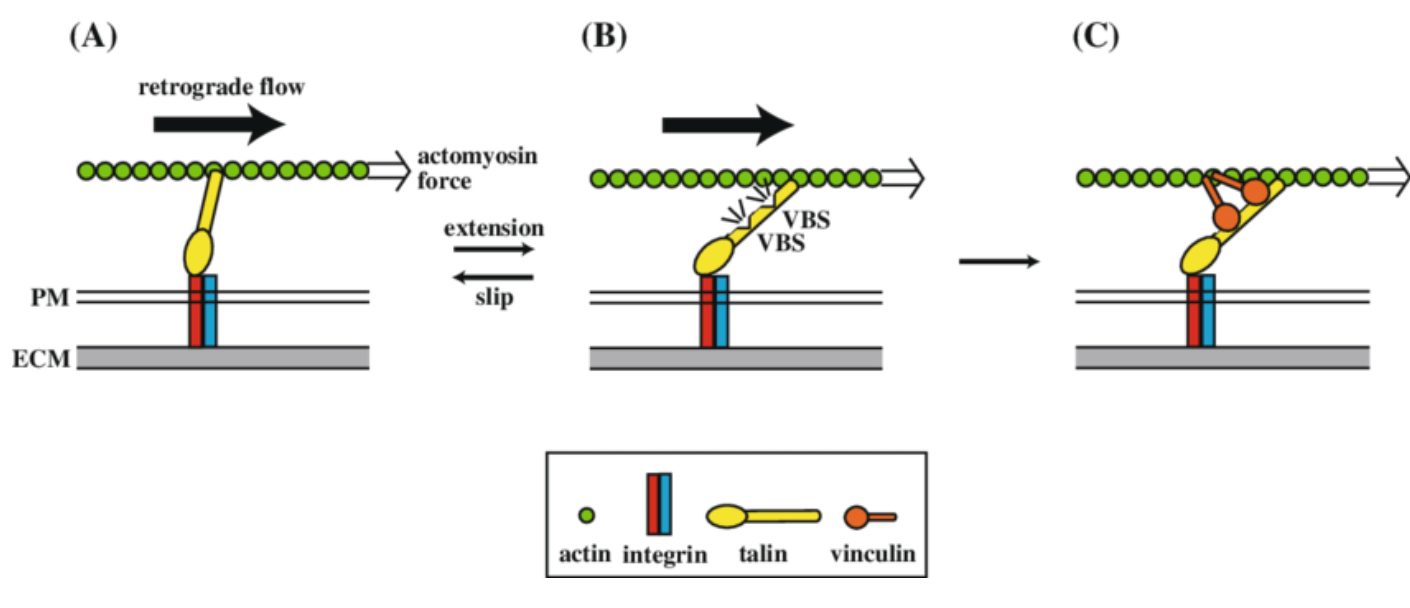 poisioning (gastroenteritis). Certain bacteria produce a toxin called Cytolethal distending Toxin. (CtDT). The immune system reacts to this CtDT toxin, and the antibodies cross react with Vinculin, which is a structure in your small intestines. So this could also be called “Post Infectious IBS”. If there’s not proper motility of the cells lining the small intestine, this will often lead to SIBO, or small intestinal bacterial overgrowth. That could lead to bloating, diarrhea, etc.
poisioning (gastroenteritis). Certain bacteria produce a toxin called Cytolethal distending Toxin. (CtDT). The immune system reacts to this CtDT toxin, and the antibodies cross react with Vinculin, which is a structure in your small intestines. So this could also be called “Post Infectious IBS”. If there’s not proper motility of the cells lining the small intestine, this will often lead to SIBO, or small intestinal bacterial overgrowth. That could lead to bloating, diarrhea, etc.
So, ask your doctor to test you for Vinculin antibodies. If you have vinculin antibodies, then your IBS should be treated like an autoimmune condition. This would change the treatment protocol somewhat.
Food allergies can play a role in IBS. I don’t put a lot of faith in food allergy testing because the results can be very unreliable. If you’re allergic to a lot of different foods, then it just means that you have a lot of intestinal inflammation, and you might need to be on a gut-healing protocol for a while.
One of the things that’s changed dramatically in our diet in the last 150 years is the types of fats we’re consuming. Modern seed oils create imbalances in omega-6 to omega-3 ratio, and do not provide arachadonic acid in adaquate quantities. Arachadonic acid is a precursor to prostaglandins, which regulate the inflammatory process. Although most prostaglandins are considered to be “pro-inflammatory”, it’s more correct to say that prostaglandins regulate inflammation.
A diet that’s low in Arachadonic acid can cause disregulated gut inflammation, especially if there are other inflammatory triggers present. This is also why I encourage people NOT to take anti-inflammatory medicines such as Ibuprofen. NSAIDS, and most other pain medications block inflammation by blocking these prostaglandins, but can interfere with prostaglandin signaling, prevent the resolution of inflamation. This is likely one reason for the increase in food allergies.
There are a lot more chemicals in our environment than ever before. From GMO grains, herbicides, thickeners, plastics, medications, and poor quality foods. Chemicals cause imbalances in hormones, and disrupt gut bacteria.
Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) is very common in IBS. And a stool test is not going to tell you whether or not you have SIBO. If you have IBS, you can assume you have SIBO. SIBO is a form of disbiosis; and treating disbiosis will help the symptoms of IBS. A stool test such as the CDSA can also rule out other possible causes for your IBS such as parasites, enzyme insufficiency, poor gallaladder function.
Are you chewing your food completely before swallowing? Do you eat too quickly? Addressing the stomach should be #1 on the list, because if your stomach can’t do its job well, it will affect everything below it. Eat slowly, and chew your food well. Take a bi-phasic digestive enzyme. Use digestive bitters. When we’re under stress, digestion takes a back-seat to the stress response. This results in the stomach not producing enough acid. With insufficient stomach acid, proteins are not properly digested, and these un-digested proteins are fermented in the lower intestinal track, resulting in bloating, discomfort, and inflammation. Make sure you stay well hydrated, with water and electrolytes. You need plenty of salt to make stomach acid.
Consider the low-FODMAP diet. FODMAPS are starches that are healthy, but can feed pathogenic bacteria. This will eliminate a lot of healthy foods, but it might be necessary in the short term until symptoms improve.
Eliminate foods that make you feel worse! If you have an allergy to a food, you’ll have to remove it, at least in the short term. When you get some resolution of symptoms, re-do the allergy test, and the results will be more accurate. Grains contain lectins which are hard to digest. If you react to starches in general, consider testing for SIBO.
Fungal infections can cause IBS. If the stool test shows zero yeast, it likely means that the immune system is reacting to yeast. You might need to be on a low starch diet, and take a probiotic containing S. boulardii. Low dose immunotherpy (LDI) can be very helpful at removing food allergies. That’s not the same as the “allergy shots”. LDI uses homeopathic preparations of allegenic substances. For example, if your IBS is caused by an allergy to yeast, you could be given a homeopathic dose of yeast. It takes a long time and much trial and error to get the right dose, but it can be very effective. “Allergy shots” are a primitive, outdated therapy that works similar to vaccination. Unfortunately I’m not aware of any doctors here in the South that use LDI, but there are many on the West coast that consult remotely, and it’s common in many other countries.
Consider nervous system imbalance. Someone who is chronically stressed or anxious will unconciously suppress their digestive function. Magnesium and potassium are helpful in the short term for promoting calm. Nervine herbs, such as passionflower or skullcap extract can work wonders. In extreme cases, I’ve used Kava to relieve anxiety. Stress can deplete other minerals and vitamins, such as vitamin B5. If anxiety is a problem, consider a good quality b-complex vitamin, and minerals. Bone broth is a good source of minerals and collagen.
The Elemental Diet is an easy-to-digest protein powder designed to be anti-inflammatory. It’s expensive, but possibly helpful in the short term, especially if you’re having trouble getting enough calories.
Herbal Antibiotics: I like to cook with garlic, oregono, rosemary, or any of the other aromatic herbs. These herbs have oils that have strong anti-bacterial properties. I also use a plethora of other herbal products such as berberine that have gentle antibiotic and anti-parasitic properties. These herbs will change the balance of the gut flora slowly over time. Use a small amount of baking soda when cooking. Baking soda has anti-inflammatory properties for the gut.
Probiotics might be a good short-term treatment. They could also make symptoms worse. But in the long term, I prefer to use prebiotic fibers, such as FOS, GOS, glucomannan, or inulin to promote the growth of healthy gut flora. If you have taken antibiotics recently, you’ll need to work extra hard on gut health.
Hyperimmune egg protein is often helpful for IBS. I’ve never tried it, but let me know if you do. It contains antibodies against certain bacteria.
Any inflammation in the gut can cause a slow gallbladder function, since the gallbladder is triggered by endogenous peptides produced in the border of the upper small intestine. If you have gallbladder symptoms, you can take supplements to ease symptoms. Cooked beets are easy to digest, and have nutrients for supporting bile flow.
Did your symptoms start after an injury, or abdominal surgery? Accupuncture, abdominal massage, or vagal nerve stimulation can help to remove adhesions in the intestines that can affect motility. Singing, and other deep-breating exercizes stimulate the vagus nerve.
Image: Non-channel mechanosensors working at focal adhesion-stress fiber complex – Scientific Figure on ResearchGate. Available from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/A-model-for-force-dependent-regulation-of-the-talin-vinculin-binding-at-FAs-and-anchoring_fig2_263433124 [accessed 22 Jun, 2023]